Class Turtle
Hierarchy
- EventEmitter
- Turtle
Index
Constructors
Properties
Accessors
Methods
Constructors
constructor
- new
Turtle(context, options?): Turtle -
Parameters
-
context: CanvasRenderingContext2D
-
Optionaloptions: TurtleOptions
Returns Turtle
-
Properties
Private angle
The current angle of the turtle.
Private color
The Color object representing the current color of the turtle.
Readonly ctx
The turtle's Canvas 2D context.
Optional delay
The delay in ms between each steps.
Private hidden
Wether or not the turtle is hidden.
Private Optional interval
The timer identifier for the step interval.
Private pen
Determines if the turtle draws on the canvas or not.
Private position
The current X/Y position of the turtle on the canvas.
Private Optional pre
Canvas Image data before drawing the turtle.
Private shape
The shape of the turtle which is drawn with the .draw method.
Represented by an array of 2D vertices (X/Y coordinates) defining the boundaries of the shape.
Private step
Wether or not the Turtle is currently perfoming a step.
Use .inStep instead.
Private step
Wether or not the Turtle is in Step by Step mode. Enabled using setDelay.
Private steps
The queue of steps do execute.
Private width
The current width of the turtle's drawing.
Private wrap
Wether or not to wrap the turtle around the canvas. The turtle goes around when overflowing.
Static Readonly capture
Value: Symbol.for('nodejs.rejection')
See how to write a custom rejection handler.
Since
v13.4.0, v12.16.0
Static capture
Value: boolean
Change the default captureRejections option on all new EventEmitter objects.
Since
v13.4.0, v12.16.0
Static default
By default, a maximum of 10 listeners can be registered for any single
event. This limit can be changed for individual EventEmitter instances
using the emitter.setMaxListeners(n) method. To change the default
for allEventEmitter instances, the events.defaultMaxListenersproperty can be used. If this value is not a positive number, a RangeErroris thrown.
Take caution when setting the events.defaultMaxListeners because the
change affects allEventEmitter instances, including those created before
the change is made. However, calling emitter.setMaxListeners(n) still has
precedence over events.defaultMaxListeners.
This is not a hard limit. The EventEmitter instance will allow
more listeners to be added but will output a trace warning to stderr indicating
that a "possible EventEmitter memory leak" has been detected. For any singleEventEmitter, the emitter.getMaxListeners() and emitter.setMaxListeners()methods can be used to
temporarily avoid this warning:
import { EventEmitter } from 'node:events';
const emitter = new EventEmitter();
emitter.setMaxListeners(emitter.getMaxListeners() + 1);
emitter.once('event', () => {
// do stuff
emitter.setMaxListeners(Math.max(emitter.getMaxListeners() - 1, 0));
});
The --trace-warnings command-line flag can be used to display the
stack trace for such warnings.
The emitted warning can be inspected with process.on('warning') and will
have the additional emitter, type, and count properties, referring to
the event emitter instance, the event's name and the number of attached
listeners, respectively.
Its name property is set to 'MaxListenersExceededWarning'.
Since
v0.11.2
Static Readonly error
This symbol shall be used to install a listener for only monitoring 'error'events. Listeners installed using this symbol are called before the regular'error' listeners are called.
Installing a listener using this symbol does not change the behavior once an'error' event is emitted. Therefore, the process will still crash if no
regular 'error' listener is installed.
Since
v13.6.0, v12.17.0
Accessors
Private in
- get inStep(): boolean
-
Wether or not the turtle is doing a step.
Returns boolean
Private line
- set lineCap(cap): void
-
The current lineCap value of the Canvas.
Parameters
-
cap: LineCap
Returns void
-
Methods
Optional [capture
add
Private add
clear
Private do
draw
draw
- draw
Grid(separations): Turtle -
Draws a grid on the Canvas. Pretty useful to be precise.
Example
turtle.clear().drawGrid(2);
turtle.clear().drawGrid(3);
turtle.clear().drawGrid(4);
turtle.clear().drawGrid(5);
turtle.clear().drawGrid(6);
turtle.clear().drawGrid(7);
turtle.clear().drawGrid(8);
Parameters
-
separations: number
The number of separations on the grid.
Returns Turtle
For method chaining.
-
emit
- emit<U>(event, ...args): boolean
-
Type Parameters
-
U extends keyof TurtleEvents
Parameters
-
event: U
-
Rest...args: Parameters<TurtleEvents[U]>
Returns boolean
-
event
- event
Names(): (string | symbol)[] -
Returns an array listing the events for which the emitter has registered listeners. The values in the array are strings or
Symbols.import { EventEmitter } from 'node:events';
const myEE = new EventEmitter();
myEE.on('foo', () => {});
myEE.on('bar', () => {});
const sym = Symbol('symbol');
myEE.on(sym, () => {});
console.log(myEE.eventNames());
// Prints: [ 'foo', 'bar', Symbol(symbol) ]Since
v6.0.0
Returns (string | symbol)[]
expose
- expose(obj, remap?): Turtle
-
Expose the Turtle's methods onto an object. This is very useful for example when using it with the
windowobject, abstracting method calls to simple functions calls.Parameters
-
obj: any
Any JavaScript Object
-
Optionalremap: ExposeRemapA remap object to remap method's names
Returns Turtle
For method chaining.
-
forward
get
- get
Max Listeners(): number -
Returns the current max listener value for the
EventEmitterwhich is either set byemitter.setMaxListeners(n)or defaults to defaultMaxListeners.Since
v1.0.0
Returns number
goto
hide
invert
left
listener
- listener
Count(eventName, listener?): number -
Returns the number of listeners listening for the event named
eventName. Iflisteneris provided, it will return how many times the listener is found in the list of the listeners of the event.Since
v3.2.0
Parameters
-
eventName: string | symbol
The name of the event being listened for
-
Optionallistener: FunctionThe event handler function
Returns number
-
listeners
- listeners(eventName): Function[]
-
Returns a copy of the array of listeners for the event named
eventName.server.on('connection', (stream) => {
console.log('someone connected!');
});
console.log(util.inspect(server.listeners('connection')));
// Prints: [ [Function] ]Since
v0.1.26
Parameters
-
eventName: string | symbol
Returns Function[]
-
Private next
off
on
- on<U>(event, listener): Turtle
-
Type Parameters
-
U extends keyof TurtleEvents
Parameters
-
event: U
-
listener: TurtleEvents[U]
Returns Turtle
-
once
- once(eventName, listener): Turtle
-
Adds a one-time
listenerfunction for the event namedeventName. The next timeeventNameis triggered, this listener is removed and then invoked.server.once('connection', (stream) => {
console.log('Ah, we have our first user!');
});Returns a reference to the
EventEmitter, so that calls can be chained.By default, event listeners are invoked in the order they are added. The
emitter.prependOnceListener()method can be used as an alternative to add the event listener to the beginning of the listeners array.import { EventEmitter } from 'node:events';
const myEE = new EventEmitter();
myEE.once('foo', () => console.log('a'));
myEE.prependOnceListener('foo', () => console.log('b'));
myEE.emit('foo');
// Prints:
// b
// aSince
v0.3.0
Parameters
-
eventName: string | symbol
The name of the event.
-
listener: ((...args) => void)
The callback function
-
- (...args): void
-
Parameters
-
Rest...args: any[]
Returns void
-
-
Returns Turtle
-
prepend
- prepend
Listener(eventName, listener): Turtle -
Adds the
listenerfunction to the beginning of the listeners array for the event namedeventName. No checks are made to see if thelistenerhas already been added. Multiple calls passing the same combination ofeventNameandlistenerwill result in thelistenerbeing added, and called, multiple times.server.prependListener('connection', (stream) => {
console.log('someone connected!');
});Returns a reference to the
EventEmitter, so that calls can be chained.Since
v6.0.0
Parameters
-
eventName: string | symbol
The name of the event.
-
listener: ((...args) => void)
The callback function
-
- (...args): void
-
Parameters
-
Rest...args: any[]
Returns void
-
-
Returns Turtle
-
prepend
- prepend
Once Listener(eventName, listener): Turtle -
Adds a one-time
listenerfunction for the event namedeventNameto the beginning of the listeners array. The next timeeventNameis triggered, this listener is removed, and then invoked.server.prependOnceListener('connection', (stream) => {
console.log('Ah, we have our first user!');
});Returns a reference to the
EventEmitter, so that calls can be chained.Since
v6.0.0
Parameters
-
eventName: string | symbol
The name of the event.
-
listener: ((...args) => void)
The callback function
-
- (...args): void
-
Parameters
-
Rest...args: any[]
Returns void
-
-
Returns Turtle
-
put
put
raw
- raw
Listeners(eventName): Function[] -
Returns a copy of the array of listeners for the event named
eventName, including any wrappers (such as those created by.once()).import { EventEmitter } from 'node:events';
const emitter = new EventEmitter();
emitter.once('log', () => console.log('log once'));
// Returns a new Array with a function `onceWrapper` which has a property
// `listener` which contains the original listener bound above
const listeners = emitter.rawListeners('log');
const logFnWrapper = listeners[0];
// Logs "log once" to the console and does not unbind the `once` event
logFnWrapper.listener();
// Logs "log once" to the console and removes the listener
logFnWrapper();
emitter.on('log', () => console.log('log persistently'));
// Will return a new Array with a single function bound by `.on()` above
const newListeners = emitter.rawListeners('log');
// Logs "log persistently" twice
newListeners[0]();
emitter.emit('log');Since
v9.4.0
Parameters
-
eventName: string | symbol
Returns Function[]
-
remove
- remove
All Listeners(event?): Turtle -
Removes all listeners, or those of the specified
eventName.It is bad practice to remove listeners added elsewhere in the code, particularly when the
EventEmitterinstance was created by some other component or module (e.g. sockets or file streams).Returns a reference to the
EventEmitter, so that calls can be chained.Since
v0.1.26
Parameters
-
Optionalevent: string | symbol
Returns Turtle
-
remove
- remove
Listener(eventName, listener): Turtle -
Removes the specified
listenerfrom the listener array for the event namedeventName.const callback = (stream) => {
console.log('someone connected!');
};
server.on('connection', callback);
// ...
server.removeListener('connection', callback);removeListener()will remove, at most, one instance of a listener from the listener array. If any single listener has been added multiple times to the listener array for the specifiedeventName, thenremoveListener()must be called multiple times to remove each instance.Once an event is emitted, all listeners attached to it at the time of emitting are called in order. This implies that any
removeListener()orremoveAllListeners()calls after emitting and before the last listener finishes execution will not remove them fromemit()in progress. Subsequent events behave as expected.import { EventEmitter } from 'node:events';
class MyEmitter extends EventEmitter {}
const myEmitter = new MyEmitter();
const callbackA = () => {
console.log('A');
myEmitter.removeListener('event', callbackB);
};
const callbackB = () => {
console.log('B');
};
myEmitter.on('event', callbackA);
myEmitter.on('event', callbackB);
// callbackA removes listener callbackB but it will still be called.
// Internal listener array at time of emit [callbackA, callbackB]
myEmitter.emit('event');
// Prints:
// A
// B
// callbackB is now removed.
// Internal listener array [callbackA]
myEmitter.emit('event');
// Prints:
// ABecause listeners are managed using an internal array, calling this will change the position indices of any listener registered after the listener being removed. This will not impact the order in which listeners are called, but it means that any copies of the listener array as returned by the
emitter.listeners()method will need to be recreated.When a single function has been added as a handler multiple times for a single event (as in the example below),
removeListener()will remove the most recently added instance. In the example theonce('ping')listener is removed:import { EventEmitter } from 'node:events';
const ee = new EventEmitter();
function pong() {
console.log('pong');
}
ee.on('ping', pong);
ee.once('ping', pong);
ee.removeListener('ping', pong);
ee.emit('ping');
ee.emit('ping');Returns a reference to the
EventEmitter, so that calls can be chained.Since
v0.1.26
Parameters
-
eventName: string | symbol
-
listener: ((...args) => void)
-
- (...args): void
-
Parameters
-
Rest...args: any[]
Returns void
-
-
Returns Turtle
-
reset
Private reset
restore
- restore
Image Data(): Turtle -
Restores the image from preDrawData.
Returns Turtle
For method chaining.
right
save
- save
Image Data(): Turtle -
Saves the current image into preDrawData.
Returns Turtle
For method chaining.
set
set
- set
Color(red, green, blue, alpha?): Turtle -
Sets a new color to be used for drawing.
Example
turtle.setColor(255, 0, 0); // red
turtle.setColor(0, 255, 0, 0.5); // semi-transparent greenParameters
-
red: number
The red value of the color.
-
green: number
The green value of the color.
-
blue: number
The blue value of the color.
-
Optionalalpha: numberThe alpha value of the color.
Returns Turtle
For method chaining.
-
- set
Color(color): Turtle -
Sets a new color to be used for drawing.
Example
turtle.setColor('red'); // red
turtle.setColor([0, 255, 0]); // green
turtle.setColor('#ffffff'); // whiteParameters
-
color: ColorResolvable
Any value resolvable to a color.
Returns Turtle
For method chaining.
-
set
set
- set
Line Cap(cap): Turtle -
Change the line cap style of the lines being drawn.
See
Example
turtle.setLineCap('butt').goto(-50, -50).forward(100);
turtle.setLineCap('square').goto(0, -50).forward(100);
turtle.setLineCap('round').goto(50, -50).forward(100);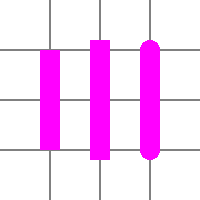
Parameters
-
cap: LineCap
Returns Turtle
For method chaining.
-
set
- set
Max Listeners(n): Turtle -
By default
EventEmitters will print a warning if more than10listeners are added for a particular event. This is a useful default that helps finding memory leaks. Theemitter.setMaxListeners()method allows the limit to be modified for this specificEventEmitterinstance. The value can be set toInfinity(or0) to indicate an unlimited number of listeners.Returns a reference to the
EventEmitter, so that calls can be chained.Since
v0.3.5
Parameters
-
n: number
Returns Turtle
-
set
set
set
- set
Width(size): Turtle -
Sets a new width to be used for drawing lines.
Example
turtle.setWidth(2).goto(-100, -50).forward(100);
turtle.setWidth(4).goto(-50, -50).forward(100);
turtle.setWidth(8).goto(0, -50).forward(100);
turtle.setWidth(16).goto(50, -50).forward(100);
turtle.setWidth(32).goto(100, -50).forward(100);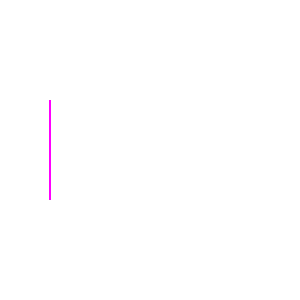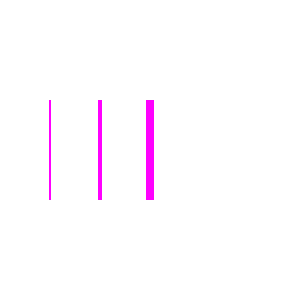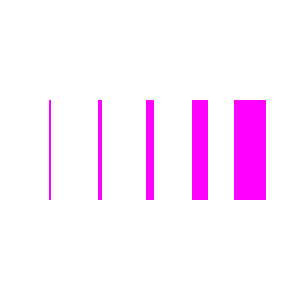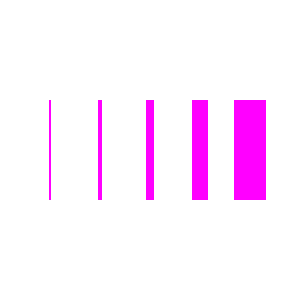
Parameters
-
size: number
Returns Turtle
For method chaining.
-
show
Static add
- add
Abort Listener(signal, resource): Disposable ExperimentalListens once to the
abortevent on the providedsignal.Listening to the
abortevent on abort signals is unsafe and may lead to resource leaks since another third party with the signal can calle.stopImmediatePropagation(). Unfortunately Node.js cannot change this since it would violate the web standard. Additionally, the original API makes it easy to forget to remove listeners.This API allows safely using
AbortSignals in Node.js APIs by solving these two issues by listening to the event such thatstopImmediatePropagationdoes not prevent the listener from running.Returns a disposable so that it may be unsubscribed from more easily.
import { addAbortListener } from 'node:events';
function example(signal) {
let disposable;
try {
signal.addEventListener('abort', (e) => e.stopImmediatePropagation());
disposable = addAbortListener(signal, (e) => {
// Do something when signal is aborted.
});
} finally {
disposable?.[Symbol.dispose]();
}
}Since
v20.5.0
Parameters
-
signal: AbortSignal
-
resource: ((event) => void)
-
- (event): void
-
Parameters
-
event: Event
Returns void
-
-
Returns Disposable
Disposable that removes the
abortlistener.-
Static get
- get
Event Listeners(emitter, name): Function[] -
Returns a copy of the array of listeners for the event named
eventName.For
EventEmitters this behaves exactly the same as calling.listenerson the emitter.For
EventTargets this is the only way to get the event listeners for the event target. This is useful for debugging and diagnostic purposes.import { getEventListeners, EventEmitter } from 'node:events';
{
const ee = new EventEmitter();
const listener = () => console.log('Events are fun');
ee.on('foo', listener);
console.log(getEventListeners(ee, 'foo')); // [ [Function: listener] ]
}
{
const et = new EventTarget();
const listener = () => console.log('Events are fun');
et.addEventListener('foo', listener);
console.log(getEventListeners(et, 'foo')); // [ [Function: listener] ]
}Since
v15.2.0, v14.17.0
Parameters
-
emitter: EventEmitter | _DOMEventTarget
-
name: string | symbol
Returns Function[]
-
Static get
- get
Max Listeners(emitter): number -
Returns the currently set max amount of listeners.
For
EventEmitters this behaves exactly the same as calling.getMaxListenerson the emitter.For
EventTargets this is the only way to get the max event listeners for the event target. If the number of event handlers on a single EventTarget exceeds the max set, the EventTarget will print a warning.import { getMaxListeners, setMaxListeners, EventEmitter } from 'node:events';
{
const ee = new EventEmitter();
console.log(getMaxListeners(ee)); // 10
setMaxListeners(11, ee);
console.log(getMaxListeners(ee)); // 11
}
{
const et = new EventTarget();
console.log(getMaxListeners(et)); // 10
setMaxListeners(11, et);
console.log(getMaxListeners(et)); // 11
}Since
v19.9.0
Parameters
-
emitter: EventEmitter | _DOMEventTarget
Returns number
-
Static listener
- listener
Count(emitter, eventName): number -
A class method that returns the number of listeners for the given
eventNameregistered on the givenemitter.import { EventEmitter, listenerCount } from 'node:events';
const myEmitter = new EventEmitter();
myEmitter.on('event', () => {});
myEmitter.on('event', () => {});
console.log(listenerCount(myEmitter, 'event'));
// Prints: 2Since
v0.9.12
Deprecated
Since v3.2.0 - Use
listenerCountinstead.Parameters
-
emitter: EventEmitter
The emitter to query
-
eventName: string | symbol
The event name
Returns number
-
Static on
- on(emitter, eventName, options?): AsyncIterableIterator<any>
-
import { on, EventEmitter } from 'node:events';
import process from 'node:process';
const ee = new EventEmitter();
// Emit later on
process.nextTick(() => {
ee.emit('foo', 'bar');
ee.emit('foo', 42);
});
for await (const event of on(ee, 'foo')) {
// The execution of this inner block is synchronous and it
// processes one event at a time (even with await). Do not use
// if concurrent execution is required.
console.log(event); // prints ['bar'] [42]
}
// Unreachable hereReturns an
AsyncIteratorthat iterateseventNameevents. It will throw if theEventEmitteremits'error'. It removes all listeners when exiting the loop. Thevaluereturned by each iteration is an array composed of the emitted event arguments.An
AbortSignalcan be used to cancel waiting on events:import { on, EventEmitter } from 'node:events';
import process from 'node:process';
const ac = new AbortController();
(async () => {
const ee = new EventEmitter();
// Emit later on
process.nextTick(() => {
ee.emit('foo', 'bar');
ee.emit('foo', 42);
});
for await (const event of on(ee, 'foo', { signal: ac.signal })) {
// The execution of this inner block is synchronous and it
// processes one event at a time (even with await). Do not use
// if concurrent execution is required.
console.log(event); // prints ['bar'] [42]
}
// Unreachable here
})();
process.nextTick(() => ac.abort());Since
v13.6.0, v12.16.0
Parameters
-
emitter: EventEmitter
-
eventName: string
The name of the event being listened for
-
Optionaloptions: StaticEventEmitterOptions
Returns AsyncIterableIterator<any>
that iterates
eventNameevents emitted by theemitter -
Static once
- once(emitter, eventName, options?): Promise<any[]>
-
Creates a
Promisethat is fulfilled when theEventEmitteremits the given event or that is rejected if theEventEmitteremits'error'while waiting. ThePromisewill resolve with an array of all the arguments emitted to the given event.This method is intentionally generic and works with the web platform EventTarget interface, which has no special
'error'event semantics and does not listen to the'error'event.import { once, EventEmitter } from 'node:events';
import process from 'node:process';
const ee = new EventEmitter();
process.nextTick(() => {
ee.emit('myevent', 42);
});
const [value] = await once(ee, 'myevent');
console.log(value);
const err = new Error('kaboom');
process.nextTick(() => {
ee.emit('error', err);
});
try {
await once(ee, 'myevent');
} catch (err) {
console.error('error happened', err);
}The special handling of the
'error'event is only used whenevents.once()is used to wait for another event. Ifevents.once()is used to wait for the 'error'event itself, then it is treated as any other kind of event without special handling:import { EventEmitter, once } from 'node:events';
const ee = new EventEmitter();
once(ee, 'error')
.then(([err]) => console.log('ok', err.message))
.catch((err) => console.error('error', err.message));
ee.emit('error', new Error('boom'));
// Prints: ok boomAn
AbortSignalcan be used to cancel waiting for the event:import { EventEmitter, once } from 'node:events';
const ee = new EventEmitter();
const ac = new AbortController();
async function foo(emitter, event, signal) {
try {
await once(emitter, event, { signal });
console.log('event emitted!');
} catch (error) {
if (error.name === 'AbortError') {
console.error('Waiting for the event was canceled!');
} else {
console.error('There was an error', error.message);
}
}
}
foo(ee, 'foo', ac.signal);
ac.abort(); // Abort waiting for the event
ee.emit('foo'); // Prints: Waiting for the event was canceled!Since
v11.13.0, v10.16.0
Parameters
-
emitter: _NodeEventTarget
-
eventName: string | symbol
-
Optionaloptions: StaticEventEmitterOptions
Returns Promise<any[]>
-
- once(emitter, eventName, options?): Promise<any[]>
-
Parameters
-
emitter: _DOMEventTarget
-
eventName: string
-
Optionaloptions: StaticEventEmitterOptions
Returns Promise<any[]>
-
Static set
- set
Max Listeners(n?, ...eventTargets): void -
import { setMaxListeners, EventEmitter } from 'node:events';
const target = new EventTarget();
const emitter = new EventEmitter();
setMaxListeners(5, target, emitter);Since
v15.4.0
Parameters
-
Optionaln: numberA non-negative number. The maximum number of listeners per
EventTargetevent. -
Rest...eventTargets: (EventEmitter | _DOMEventTarget)[]
Returns void
-


A Turtle to draw on a canvas.
Example